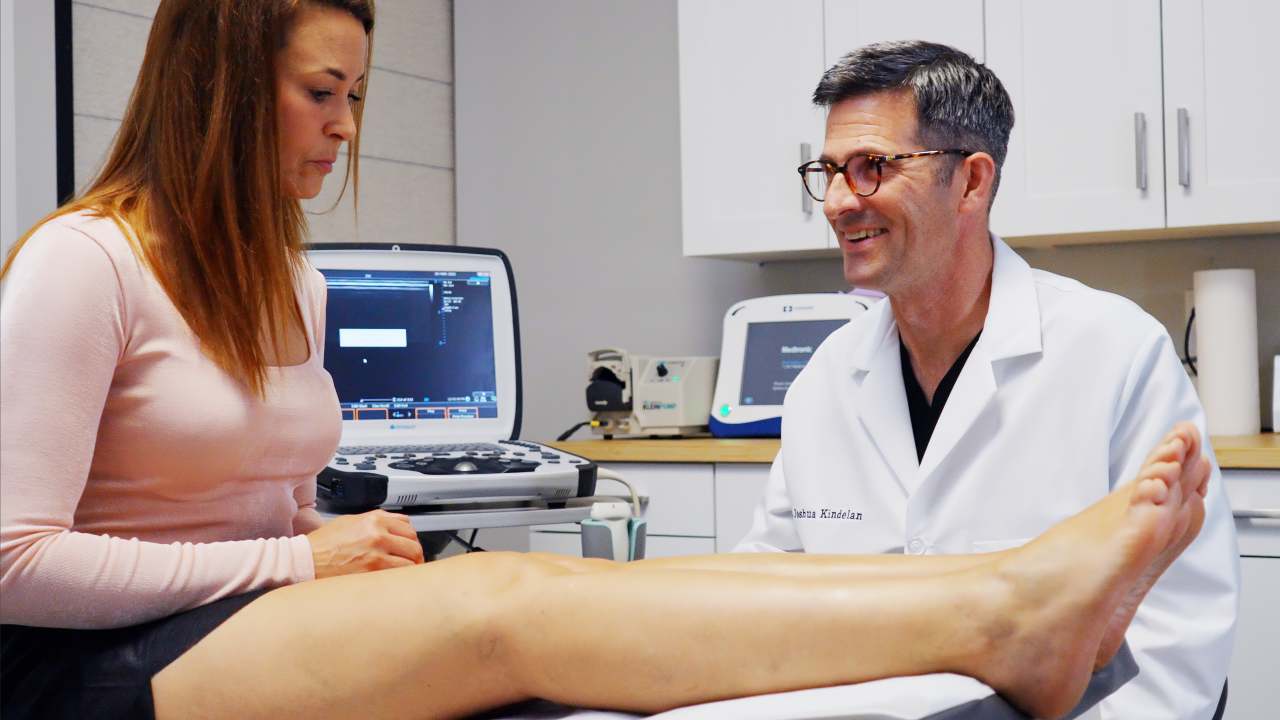
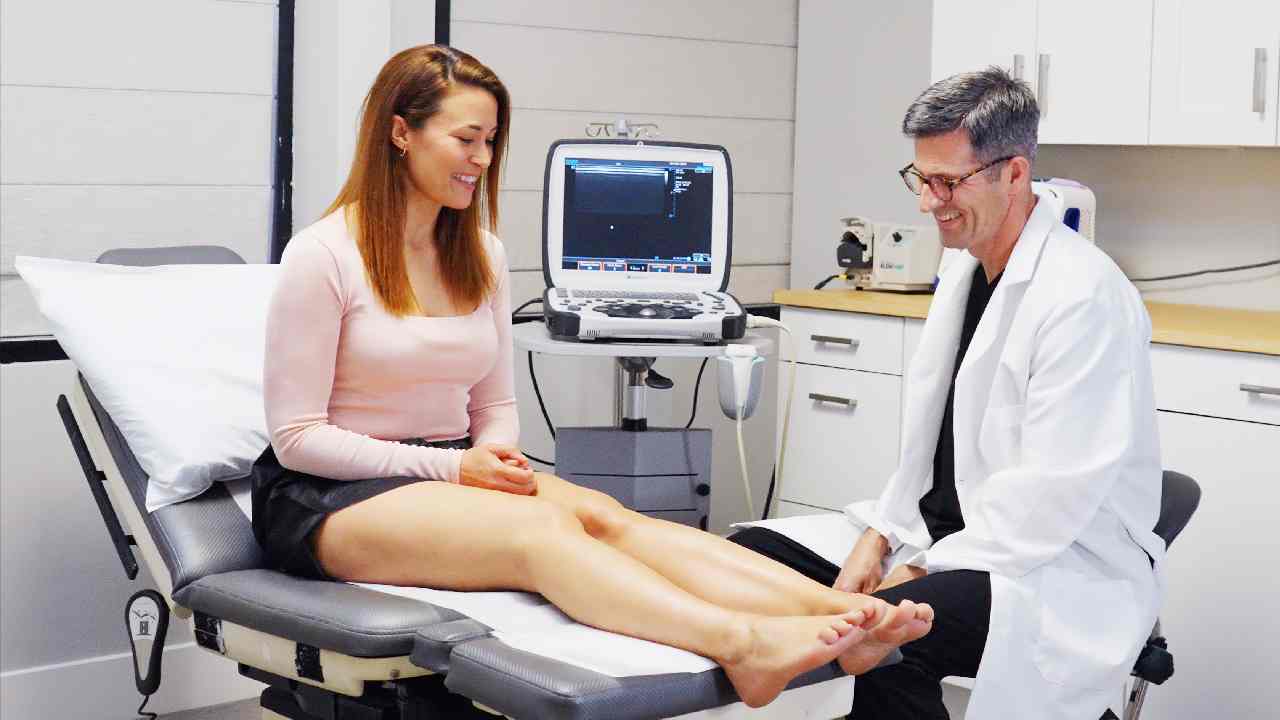
Syncope, commonly known as fainting, is a sudden and temporary loss of consciousness. This occurs due to a reduced supply of oxygen-rich blood to the brain, often linked to low blood pressure (hypotension). The causes of syncope can be cardiac, metabolic, or neurological in nature.
Two of the most common forms of fainting include:
- Orthostatic Hypotension: A sudden drop in blood pressure when transitioning from lying to standing or sitting to standing.
- Vasovagal Syncope: A reflex response that leads to fainting due to overstimulation of the vagus nerve, which slows the heart rate and dilates blood vessels.
Abnormal blood pooling in the lower extremities can exacerbate both conditions. This is a common issue in patients with varicosas o insuficiencia venosa crónica.
How Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency Contribute to Syncope
Estas venas várices occur when the valves in the veins weaken, allowing blood to flow backward and accumulate in the legs. Over time, this leads to symptoms such as swelling, discomfort, and leg heaviness.
For individuals already prone to postural hypotension, the presence of venous insufficiency can worsen the condition by causing additional blood pooling. This further reduces blood circulation to the brain, increasing the likelihood of fainting episodes.
Are you interested in getting more information about your condition or getting a treatment?
Fill the form below to start!
Managing Vasovagal Syncope and Orthostatic Hypotension
The most common treatments for managing syncope include:
- Increasing hydration to maintain adequate blood volume.
- Reevaluating chronic medications that may contribute to low blood pressure.
- Wearing medias de compresión. improves circulation and prevents blood from pooling in the legs.
Since venous insufficiency can complicate postural hypotension, specialists at Vein Treatment Clinic recommend an early evaluation for vein disease in patients experiencing recurrent fainting spells.
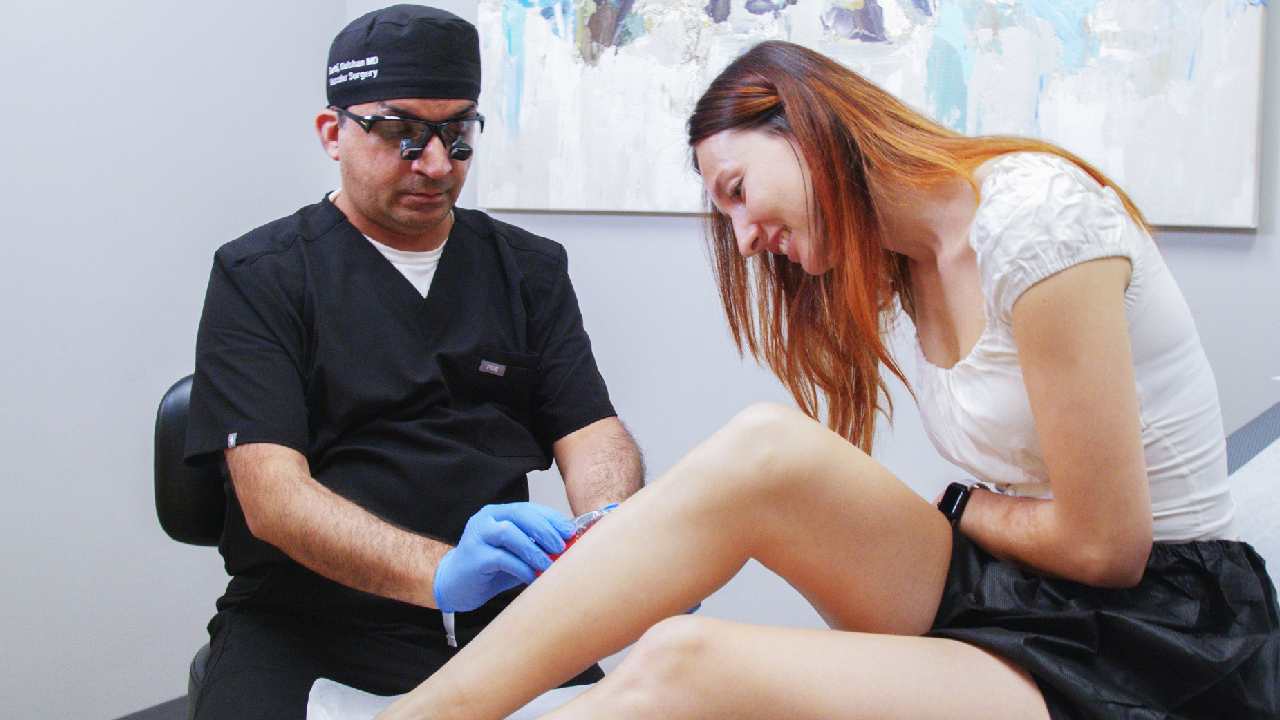
Advanced Treatments for Varicose Veins
If you suffer from varicose veins, several minimally invasive treatments can help restore proper circulation and reduce associated symptoms:
1. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Uses heat energy to close problematic veins.
- Minimally invasive with a fast recovery time.
- Requires only local anesthesia, allowing for quick recovery and minimal downtime.
- Provides long-lasting results, reducing the risk of vein recurrence.
2. Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT)
- Similar to RFA but uses laser energy to seal veins.
- Effective for larger varicose veins.
- Performed under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting.
- Helps relieve pain, swelling, and discomfort associated with varicose veins.
3. VenaSeal
- A medical adhesive is used to seal the diseased vein permanently.
- No need for compression stockings post-procedure.
- Provides immediate relief with minimal side effects.
- Suitable for patients who prefer a non-thermal, non-tumescent treatment option.
4. Sclerotherapy
- Ideal for smaller varicose and spider veins.
- Involves injecting a sclerosing agent into the affected veins, causing them to close.
- Performed quickly with no need for anesthesia.
- Can be combined with other treatments for optimal results.
Expert Varicose Vein Treatment by Dr. Sareh Rajaee
Dr. Sareh Rajaee, a leading varicose vein specialist in New Jersey, contributed to this article. Dr. Rajaee specializes in varicose vein removal and spider vein treatments using state-of-the-art techniques like radiofrequency ablation (RFA), endovenous laser therapy (EVLT), and VenaSeal.
If you are looking for a Vein Treatment Clinic in New Jersey, contact us today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Sareh Rajaee and explore your treatment options.
Final Thoughts
Syncope can be linked to chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial. If you experience fainting spells, leg swelling, or discomfort, consider an evaluation at Vein Treatment Clinic to prevent further complications and improve your quality of life.
FEATURED POSTS BY VEIN DOCTORS