How to Prevent Varicose Veins: Tips, Causes, and Treatments
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects many individuals, especially those who age or experience changes in their circulatory systems. While often seen as a cosmetic issue, varicosas can also cause discomfort and indicate underlying venous insufficiency. Understanding the role of circulation in vein health is crucial for prevention and treatment.
The circulatory system works efficiently to move blood throughout the body. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart, while veins return it. Veins contain one-way valves designed to keep blood flowing in the right direction. However, when these valves weaken, blood can pool in the lower extremities, leading to varicose veins—a condition known as venous insufficiency.
While varicose veins may not always be preventable, certain lifestyle choices and treatments can reduce your risk and minimize symptoms.
Are you interested in getting more information about your condition or getting a treatment?
Fill the form below to start!
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Several factors contribute to varicose veins, including:
-
Blood Clots (Deep Vein Thrombosis) – Restricted blood flow due to clots increases vein pressure and causes varicose veins.
-
Obesity – Extra weight places additional strain on veins, weakening the valves.
-
Pregnancy – Increased blood volume and weight gain put pressure on the leg veins, leading to varicose veins.
-
Smoking – Leads to plaque buildup in arteries and impairs circulation.
-
Muscle Weakness – Poor muscle tone slows circulation, increasing the likelihood of varicose veins.
-
Inflammation (Phlebitis) – Inflamed veins restrict blood flow and contribute to venous insufficiency.
-
Genetics – A family history of vein disease increases the risk.
-
Inactivity – Prolonged sitting or standing can lead to poor circulation and vein dysfunction.
How to Prevent Varicose Veins
While some risk factors are beyond your control, you can adopt healthy habits to support vein health and circulation:
1. Stay Active
-
Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, strengthens leg muscles.
-
Avoid sitting or standing for extended periods; move around every hour.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
-
Excess weight puts unnecessary pressure on veins, increasing the risk of valve damage.
-
A balanced diet rich in fiber and low in salt can help prevent swelling and improve circulation.
3. Avoid Smoking
-
Smoking affects blood flow and weakens vein walls, making varicose veins more likely.
4. Wear Compression Stockings
-
Compression socks improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs.
-
Proper fit is essential—consult a specialist to find the right level of compression.
5. Elevate Your Legs
-
Raise your legs above heart level for at least 15 minutes several times a day to encourage blood flow.
Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency
If you experience any of the following symptoms, consult a vein specialist for an evaluation:
- Pain, swelling, or cramping in the legs
- Heaviness or fatigue in the lower extremities
- Discoloration or thickening of the skin
- Development of ulcers near the ankles
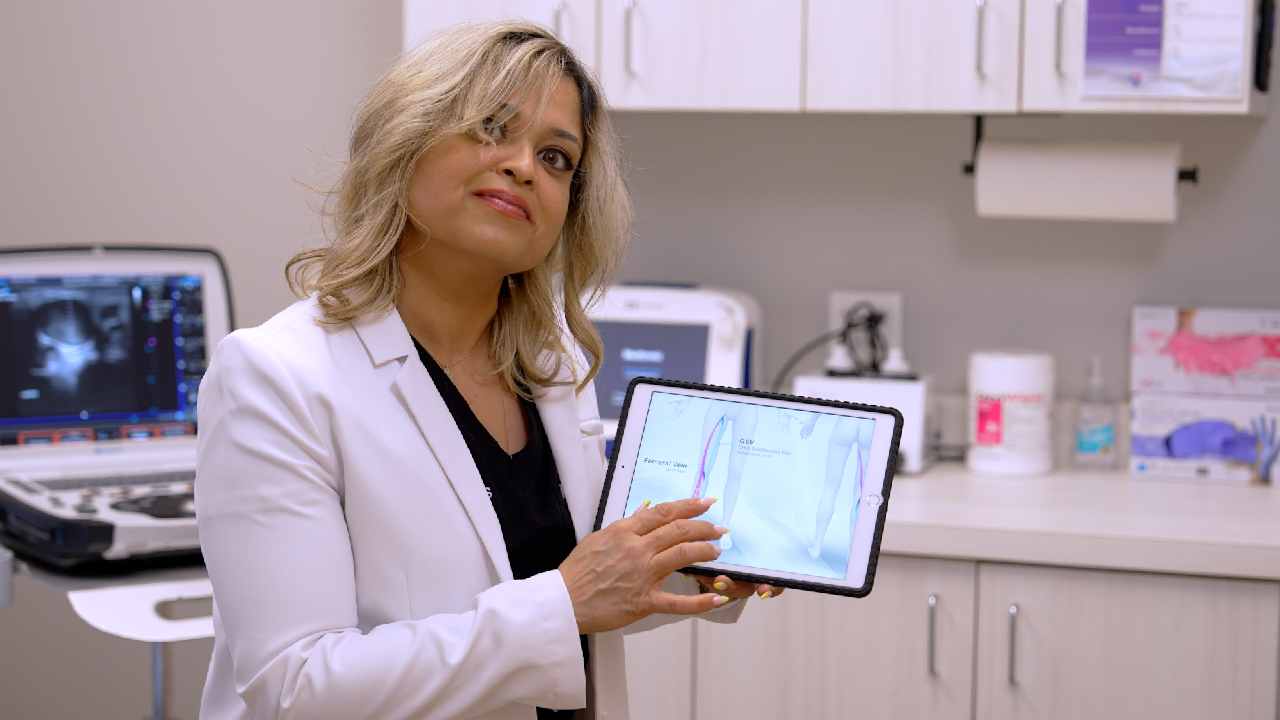
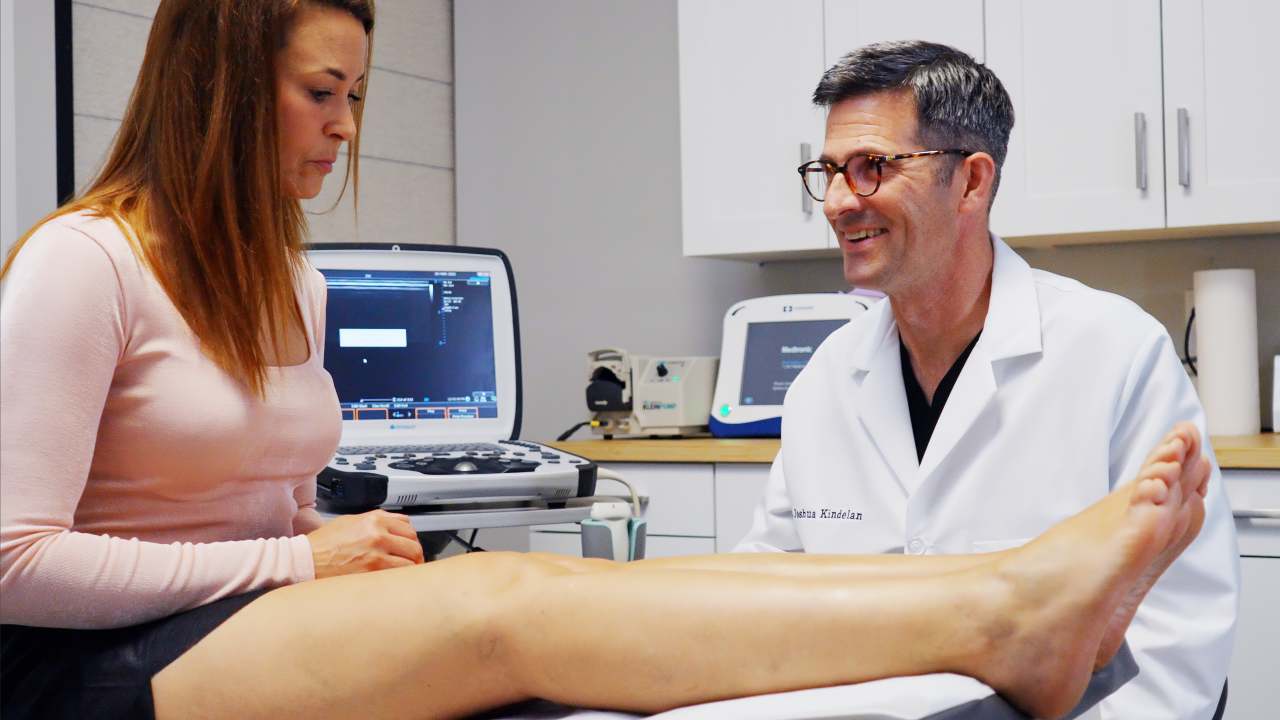
Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
A vein specialist will assess your condition through:
- Medical History Review – Understanding risk factors and symptoms.
- Physical Examination – Identifying visible vein abnormalities.
- Duplex Ultrasound – Evaluating blood flow direction and detecting blockages.
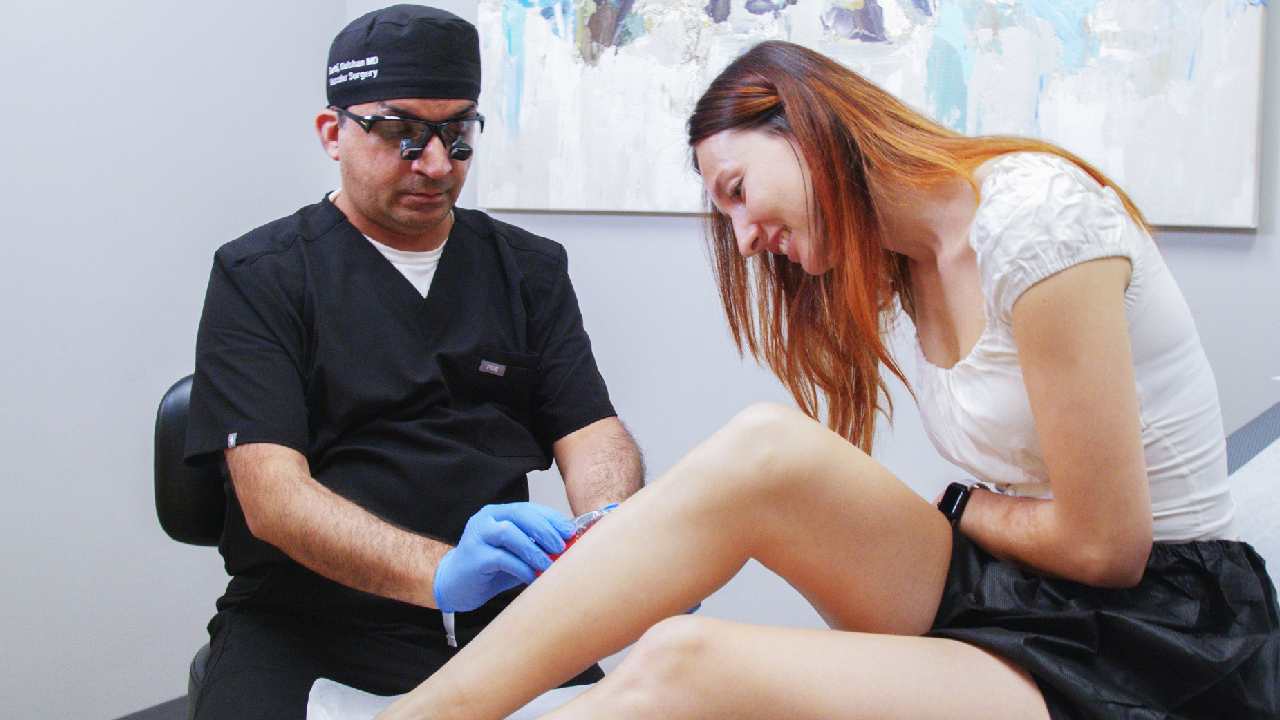
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
If lifestyle modifications are insufficient, minimally invasive treatments can effectively address varicose veins:
1. Compression Stockings
-
Apply pressure to the legs, reducing swelling and improving circulation.
2. Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) & Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
-
Use heat energy to close damaged veins, redirecting blood to healthier veins.
3. Sclerotherapy
-
A chemical injection seals off small varicose and spider veins.
4. VenaSeal
-
Uses medical adhesive to close veins without requiring compression stockings post-procedure.
5. Phlebectomy
-
Removes larger varicose veins through tiny incisions.
When to See a Specialist
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or skin changes, consult a vein doctor for personalized treatment recommendations. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
FEATURED POSTS BY VEIN DOCTORS